Acoustic Enclosures and Sound Enclosures
What is an acoustic enclosure? There are two ways to answer this question: one refers to a product and the other to a group of acoustic solutions for noise reduction. This article explains the difference between the two and covers most types of acoustic enclosures you may encounter in commercial, professional, and industrial environments.
What is an Acoustic Enclosure?
Acoustic enclosures refer to closed engineered structures specially planned and built to reduce, minimize, or attenuate noise emitted by specific equipment or machinery. They are mostly known under the appellation acoustic enclosure, but they’re also called sound enclosures and, more rarely, noise enclosures.
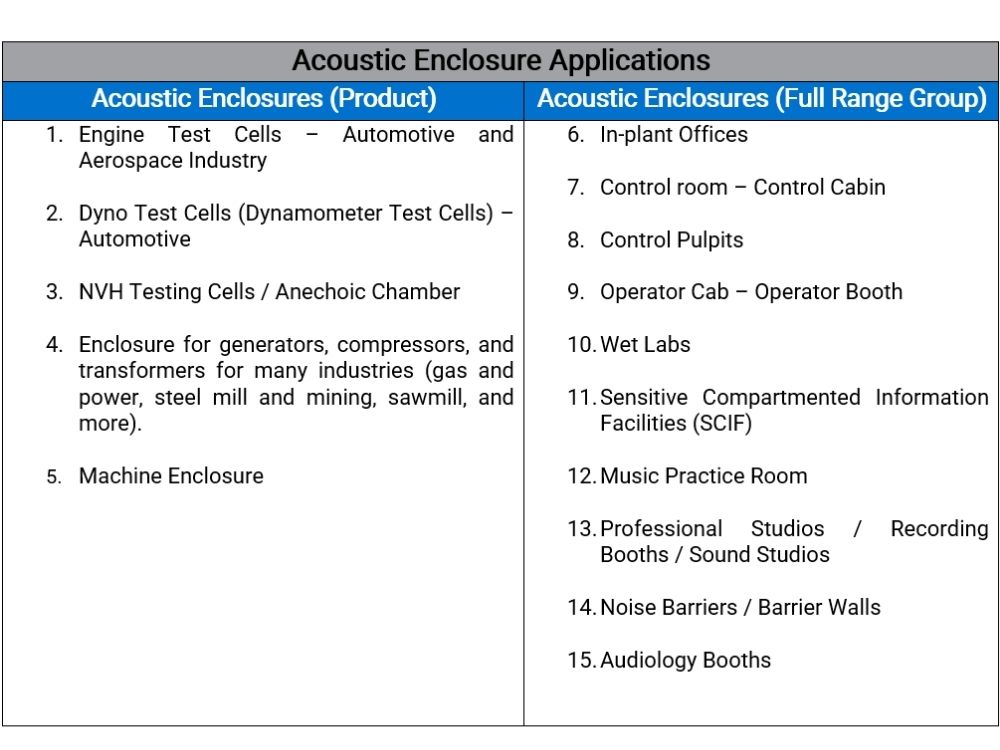
There are 2 ways to use the term acoustic enclosure.
First, to describe the product itself – an enclosure that will muffle or reduce the sound from a machine, generator, processor, metal press, or test cell. If you want to know more about it, you can read our 8 Key Elements to Design a High-Performance Acoustic Enclosure article.
Second, to describe the whole range of noise control products and solutions, including the acoustic enclosures (product). The term is used more generally to describe any acoustic enclosure, even those with operators inside. This includes control rooms, operator cabins, and even acoustic studios for post-production, video games audio, live broadcasting, and more.
Sound enclosures and acoustic enclosures come in different shapes, sizes, and specific needs in terms of noise reduction, as the noise sources or applications can change significantly from one location to another.
The design for both groups will also change a lot. For example, in a hydroelectric plant, a machine enclosure usually doesn’t require any human operating inside the enclosure. Your acoustic enclosure (product) design does not require ergonomics or comfort. There are two main concerns for acoustic enclosure designs: sound isolation (transmission loss) and easy access for equipment maintenance.
For the acoustic enclosures (full range group), it’s a different ball game! In the same plant used in the previous example, the control room or pulpit design will require particular attention to comfort, ergonomics, views on the work activities (windows), and protection from consistent noise sources. We could also add sinks, a kitchenette, or anything else to help productivity and workers who spend long hours inside the control room, operator cab, or pulpits.
The picture on the right is a chart of common applications for acoustic enclosures.
Need an Acoustic Enclosure? Call Us !
Types of Acoustic Enclosures and Noise Enclosures
1. Engine Test Cell / Dyno Test Cell / Dynamometer Test Room
The engine test cell, also known as dyno test cell or dynamometer test room, is an acoustic enclosure made to realize engine operations and tests for the automotive, aerospace, and aviation industries. For example, a test cell for an aircraft jet engine is the equipment in which performance tests are performed after an engine’s maintenance. This also verifies the working condition of each section, as well as the adjustment of each part before loading onto the aircraft via a trial run of the engine. This is the same type of process for car or aircraft engine testing.
These tests provide valuable information and cannot be influenced by external noise or sound, as the measurements must be error-free. This is why engine test cells are performed inside acoustic enclosures. This also limits the amount of noise coming out of the engine test cell to provide a comfortable and quieter workplace environment.
These acoustic enclosures can be reinforced with metal sheets to protect workers from motor failures and explosions.

2. NVH Test Enclosure
NVH testing is frequently utilized in the automobile sector to reduce, design, and inspect the interior and exterior vehicle noise or vibration. Typically, the procedure occurs during the construction of a passenger automobile.
Complete car NVH testing usually takes place in a semi-anechoic chamber, but specific car parts, such as car seats, can take place in small NVH acoustic enclosures. Car seat suppliers buy sound enclosures for their NVH testing activities, similar to the picture here.
Read the complete case study of this car seat NVH acoustic enclosure.

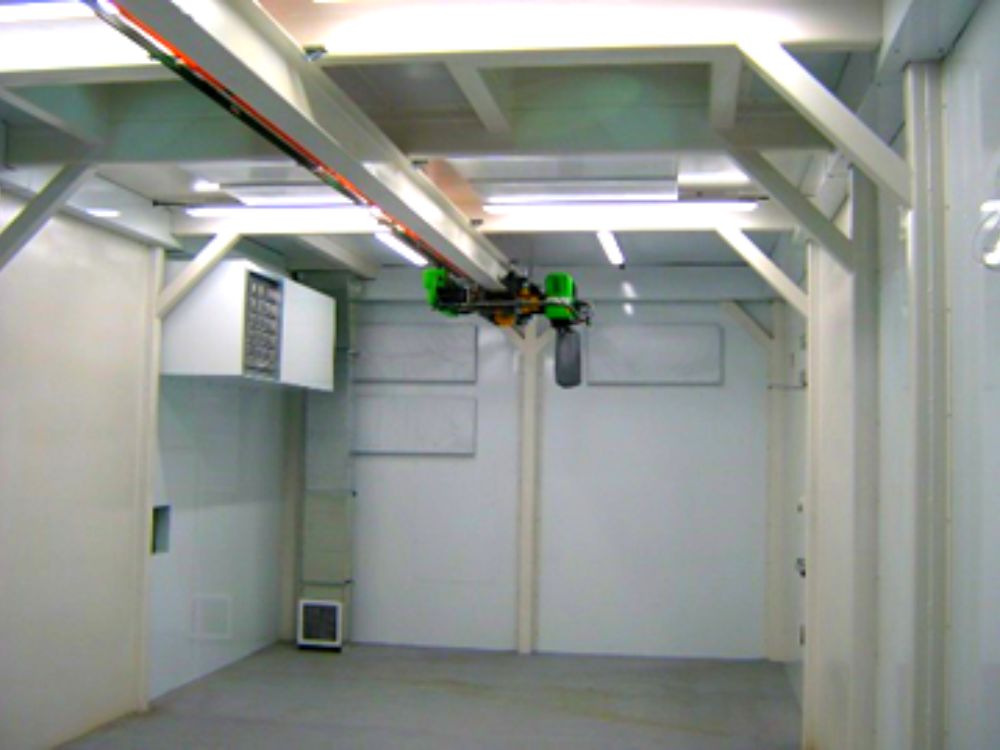
3. Acoustic Enclosure (Product)
These acoustic enclosures, in general, are pretty bulky given the large size of the equipment they cover. These sound enclosures are designed to suppress the loud noises from generators, compressors, and transformers.
Even though they might only look like big noise-reducing boxes, their engineering is no simple task. When designing an acoustic enclosure, there are various features to think of; What sound isolation (TL) do you require? How frequently do you need to access the generators or transformers daily? Do you have to deal with high, mid, or low-frequency sounds in your facility? Do you need ventilation inside the acoustic enclosure? Doing business with an experienced acoustic enclosure manufacturer will prove helpful for these complex projects.
On the right, we can see a picture of an acoustic enclosure for a generator at a hydroelectric plant.
To see acoustic enclosure (product), click on the projects below.

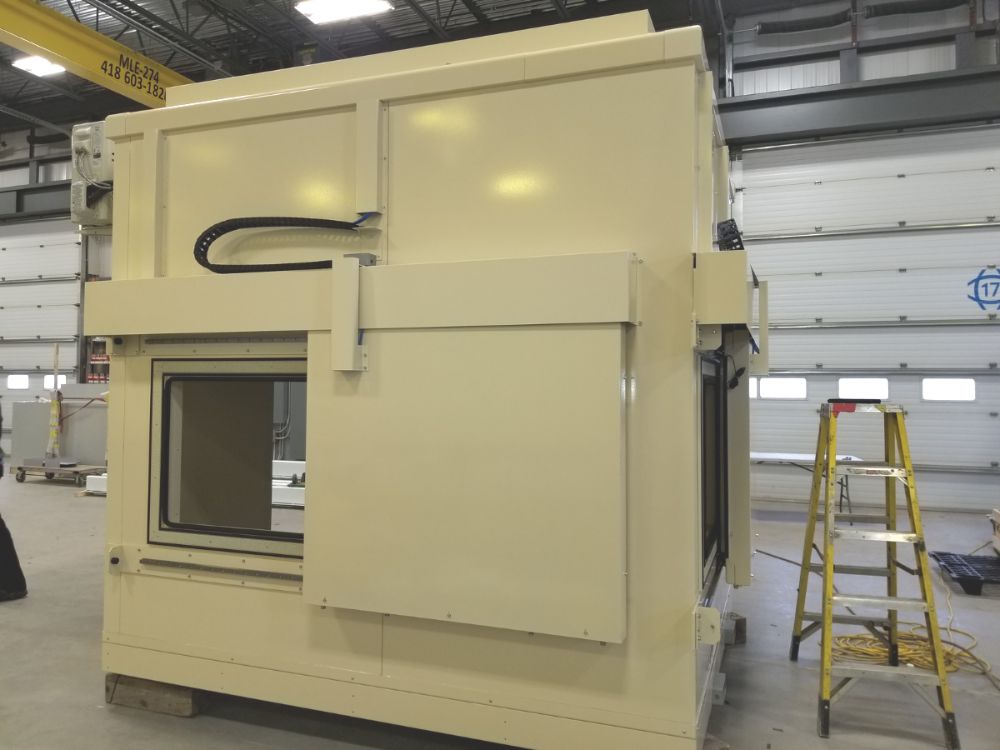
4. Partial Acoustic Enclosure (Product)
Partial acoustic enclosures (product) are designed to suppress most noises coming from generators, compressors, transformers, and the plant’s machinery but as its name states, it’s not a fully closed enclosure.
For instance, a partial enclosure can have different configurations such as
- 4 walls with no ceiling
- 2 walls with a base and ceiling
- 3 walls
- Or any particular needs
The modular noise enclosure, for example, would not be able to cover the base or the top of the acoustic enclosure; it would essentially be 4 walls made of acoustic panels. As the partial acoustic enclosure isn’t sealed, the acoustic performance cannot be as high as it would if the whole enclosure was closed.
The power transformer acoustic enclosure on the right in the picture comprises 4 modular walls, needed to deal with the low-frequency noise coming from the power transformer.
Read our Partial Acoustic Enclosure for Transformer case study for more detail on this project.
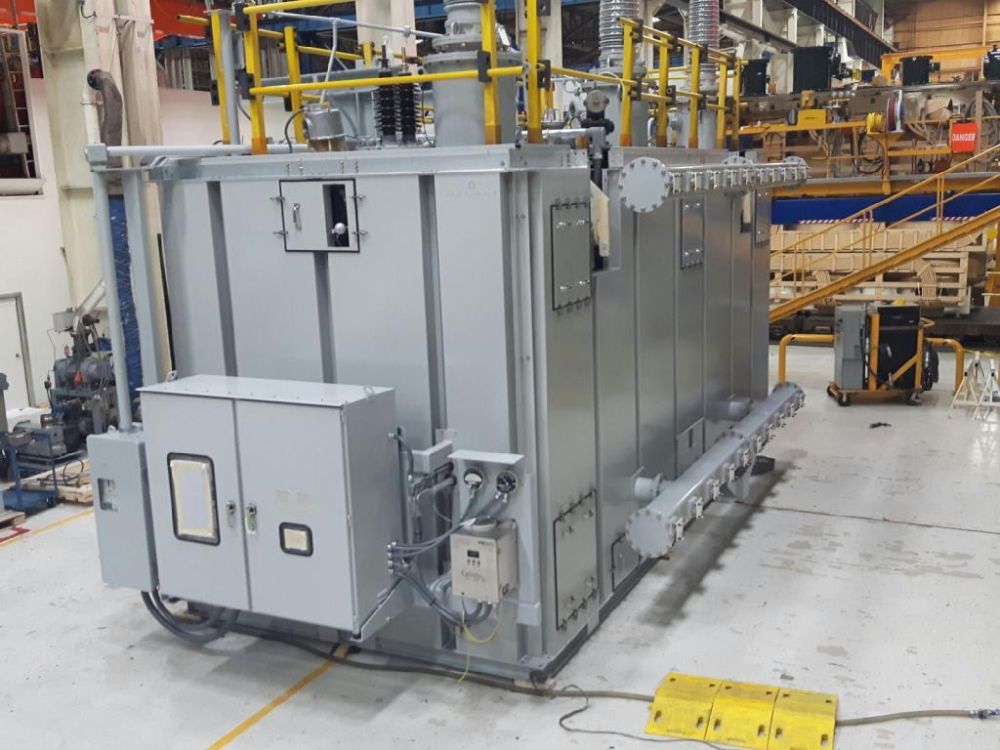

5. Machine Enclosure / Equipment Enclosure
A machine enclosure is an acoustic enclosure built around a machine or the machine’s point of operation to protect the operator from sound while shielding the equipment from damage.
Machine enclosures or equipment enclosures slightly differ from a conventional acoustic enclosure (product) as they are not only designed to minimize or reduce noise levels because they are part of the production process. This type of acoustic enclosure is usually custom-made because there are many details to consider, and it’s harder to find a standard solution that would provide all the requirements needed.
You must consider the following features in your equipment enclosure’s design:
- The visibility required within the enclosure (to view a display or a gauge)
- Hatches
- Maintenance access
- Acoustic tunnels for conveyors
- Waste and pollutant release
- Heat and humidity management
The enclosure can be tailored to the specific shape of your equipment or large enough to allow operators and maintenance personnel access to the machines.
You can see more machine enclosure projects below.
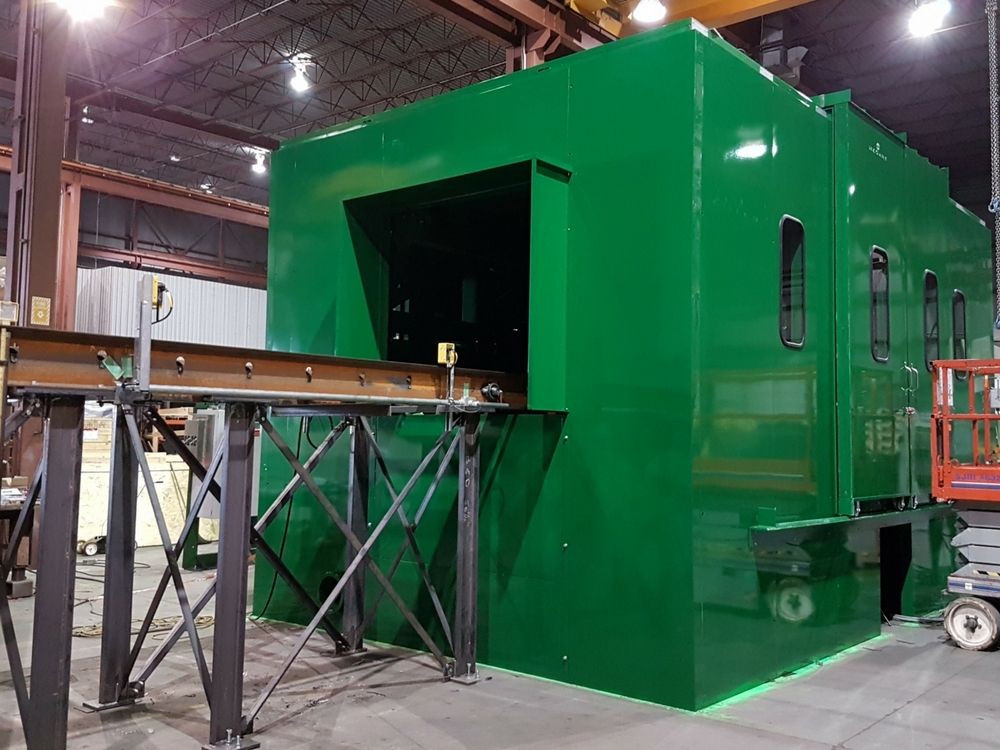

6. In-plant Offices
In-plant offices are acoustic enclosures designed to provide administrative workspace for workers and supervisors inside the plant or factory, near the manufacturing operations. Modular in-plant offices have the advantage of not disturbing production because they can be prefabricated and delivered or quickly assembled on-site. They can even be expanded easily thanks to modular panels.
This type of acoustic enclosure will provide the sound isolation you need while also offering a close look at operations, facilitating communication that will positively impact productivity.
You may also use that type of acoustic enclosure for in-plant lunchrooms, break rooms or conference rooms. You can find multiple sizes for your in-plant offices, from the small supervisor office to an entire soundproof workplace.
You can see more in-plant office projects below.
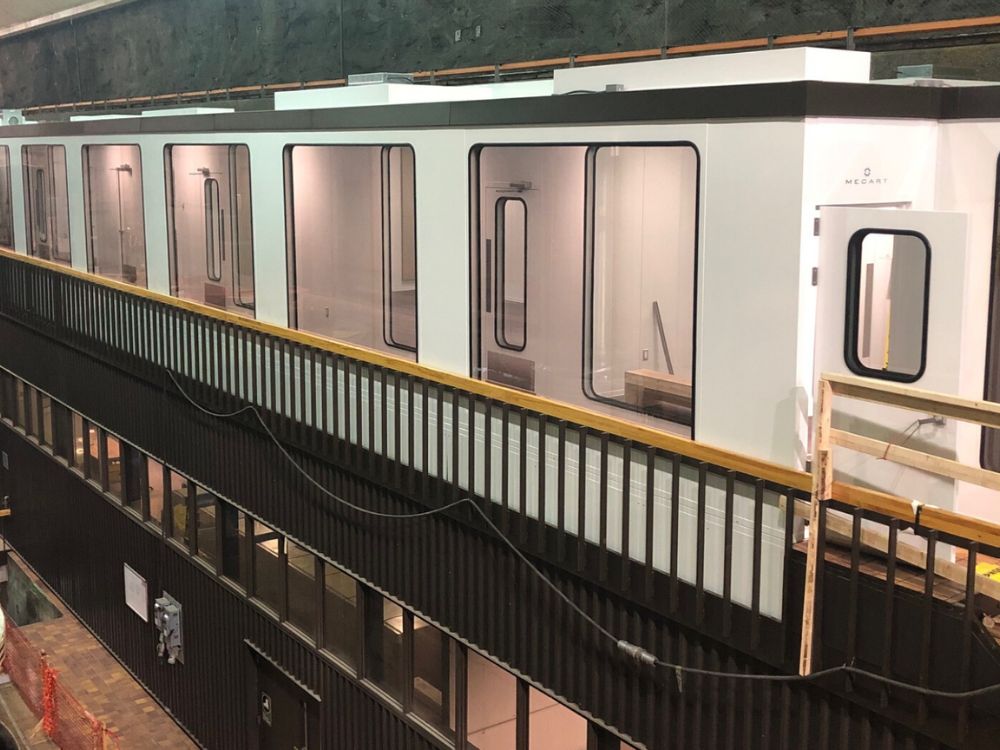

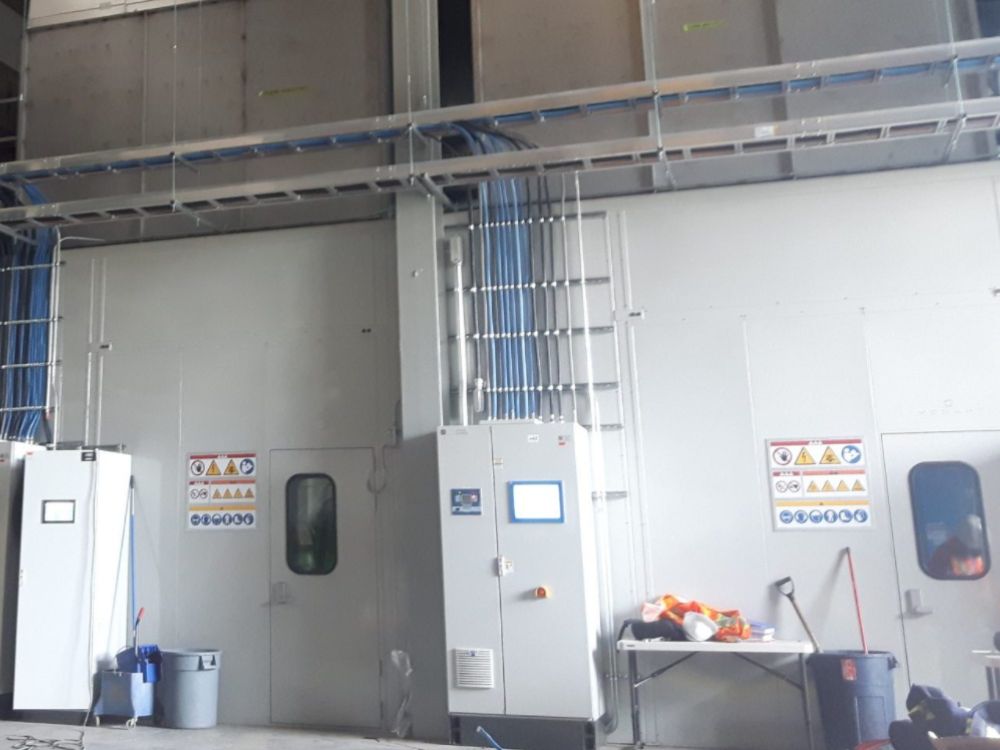
7. Control Room
A control room is an acoustic enclosure that mixes high levels of sound isolation (TL) with an extensive range of vision for good visibility and a fully fitted-out interior. They are also called control pulpits, as they are intended to manage operations inside mills and factories, although they differ slightly in some ways.
Control rooms are typically medium to large sound enclosures located directly on the bottom floor near operations or on a mezzanine within the plant. It’s common to see angled windows to provide better angles to view the operations fully. Control rooms are a central part of various products’ manufacturing and are used for different applications in many industries.
Control rooms are designed to provide a safe environment for workers and protect them from many potential dangers. Chemicals, loud equipment noise, and high heat are just a few of the possible hazards in a manufacturing plant.
It’s not rare to see these acoustic enclosures equipped with commodities such as sinks, a kitchenette, and anything else that will accommodate the workers during their working hours inside the control room. Monitors and computer screens are also part of the material you need to include in your control room design.
Most control rooms provide sound isolation (transmission loss), on average, of about 30 decibels and up to 55+ decibels. But keep in mind that most control room projects are customized and specifically designed to meet your needs.
On the right, you can see a control room for a steel manufacturing plant.
To see other Mecart control rooms , click on the projects below.
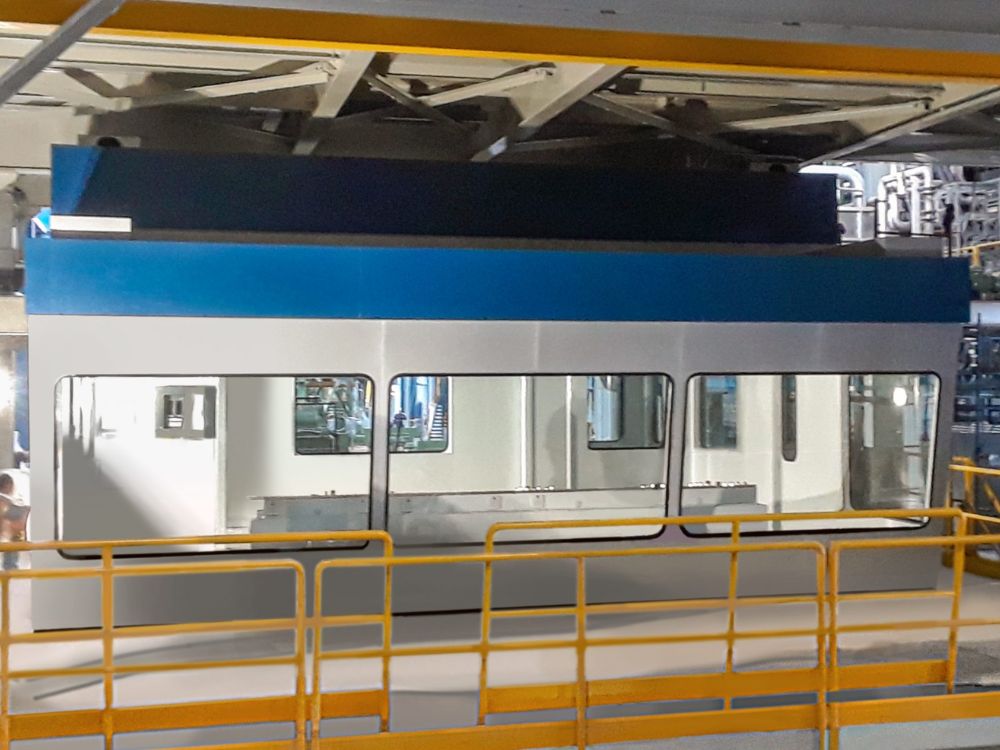

8. Operator Cab / Crane Cab / Operator Booth
The operator cabs or operator cabins look like smaller control rooms and pulpits, but they differ in their usage. An operator cab is employed for operating machines and equipment, while a control room is more for supervising operations. These acoustic enclosures are widely used to protect equipment operators from noise and harm. Operator cabs are made with thick modular steel panels to provide the proper sound isolation for your needs.
Like their control room and pulpit counterparts, the high-quality, heavy-duty materials used to construct them make them durable (25+ years) and resistant to harsh manufacturing environments.
The picture on the right is a Forkliftable Operator Cabin that can be moved easily and provides Forkliftable Operator Cabin that can be moved quickly, and that offers sound isolation (TL), on average, about 35 decibels (STC 35).
To see other operator cabs, click on the projects below.
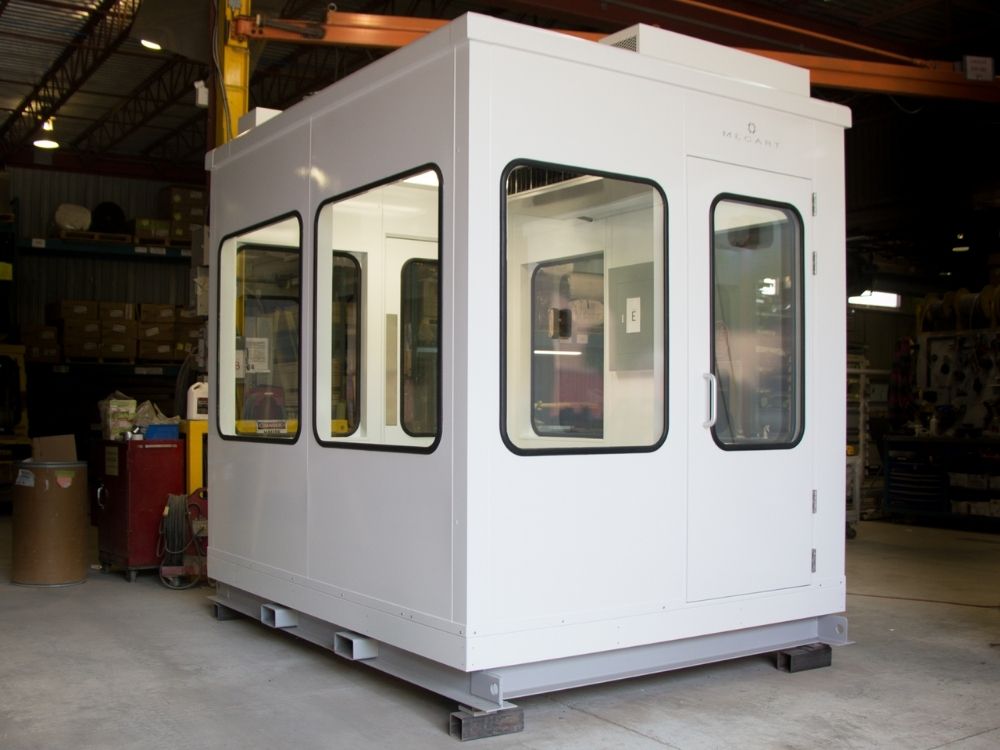

9. Control Pulpit
By definition, a control pulpit is a control room that sits on an elevated platform, such as a mezzanine. A control room and control pulpit share the same purpose, monitoring and supervising operations from a strategic position.
Control rooms, control cabins, and control pulpits are closely related; they can all be found under the same manufacturing plant’s roof if needed. A factory or mill could have only 1 or all of them. These 3 types of acoustic enclosure can be found in the following industries:
- Pulp and paper mills (forestry)
- Mining and metals (example: steel mill)
- Manufacturing (OEM, textile manufacturing)
- Gas and Power (power plant)
The different industries’ requirements might impact the design to respond to unique features, which is why Mecart’s control pulpits are custom designed.
Read the full Control Pulpits for Steel Manufacturing Plant case study.
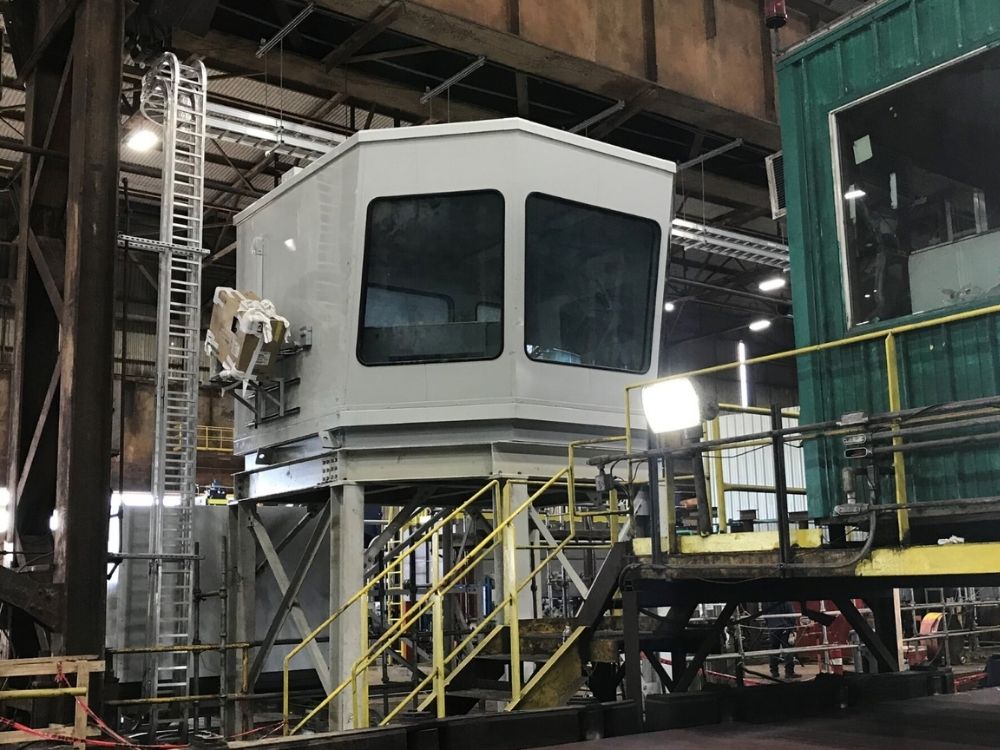

10. Wet Labs
Wet labs can be found in numerous industries but only a few applications require an acoustic sound enclosure for their wet lab testing process.
It’s the case for pulp and paper wet labs. High noise levels emanate from pulp and paper equipment and machinery inside the manufacturing plant, which becomes problematic when employees are exposed to it for an extended period.
In the pulp and paper industry, wet laboratories check pulp in its wet state for various properties such as freeness, consistency, fractionation, flake content, and others. To do those tasks in a comfortable and safe environment, wet labs also need to reduce sound and noise coming from inside the laboratory. That’s why wet labs need to be acoustic enclosures for some applications. Vibration might also cause problems for your wet lab, so this must be considered in the design.
Traditionally, these sound enclosures are built with concrete because of the well-known acoustic performances of concrete, but more and more pulp and paper companies prefer to choose a modular solution for their wet lab acoustic enclosures.
Read here the paper mill wet lab case study.
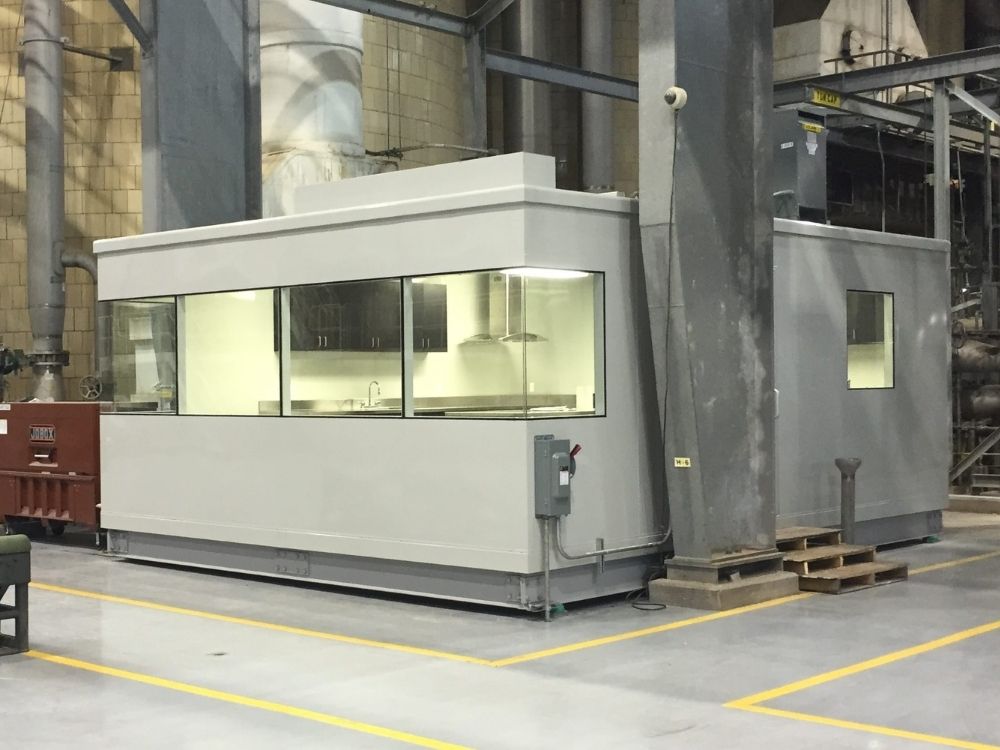

11. Music Practice Room / Music Rehearsal Space
Music practice rooms are aimed to isolate the room from external noise, reduce internally generated noises, and offer optional vibration isolation from structure-borne noise transmission.
These sound enclosures are specifically designed for music practice and rehearsal for professionals and educational purposes.
Music rehearsal spaces can be designed and built to suit all sizes, specifications, and acoustic performance needs.

12. Sensitive Compartmented Information Facilities (SCIF)
Sensitive Compartmented Information Facilities have secured areas where sensitive compartmented information may be stored, used, discussed, and/or electronically processed. SCIFs are acoustic enclosures built for government agencies, such as the military (U.S. Defense Department) or special services like the CIA. The most famous SCIF is undoubtedly the Situation Room inside the White House.
This acoustic or sound enclosure must meet precise requirements and strict specifications (specs). They are primarily modular enclosures because they can either go outside and be moved or designed to fit inside an already existing building. In other words, they use modular construction because of the flexibility and mobility it provides.
There are two important aspects to consider when designing a SCIF: explosion-proof and acoustic requirements.
First, the walls and structures of a SCIF need to be reinforced and able to withstand deflagrations and explosions.
Secondly, Sensitive Compartmented Information Facilities (SCIF) have acoustic requirements to meet to ensure that the SCIF structure’s ability to retain sound and crucial information is optimal. The US government specs have divided the acoustic performance needed into 2 Sound Group Ratings using the Sound Transmission Class (STC) descriptive value.
- Sound Group 3 – STC 45 or better. Loud speech from within the SCIF can be faintly heard but not understood outside of the SCIF. Normal speech is unintelligible with the unaided human ear.
- Sound Group 4 – STC 50 or better. Very loud sounds within the SCIF, such as loud singing, brass music, or radio at full volume, can be heard with the human ear faintly or not at all outside of the SCIF.
Source for the SCIF STC ratings: https://bit.ly/3Hp1LAm
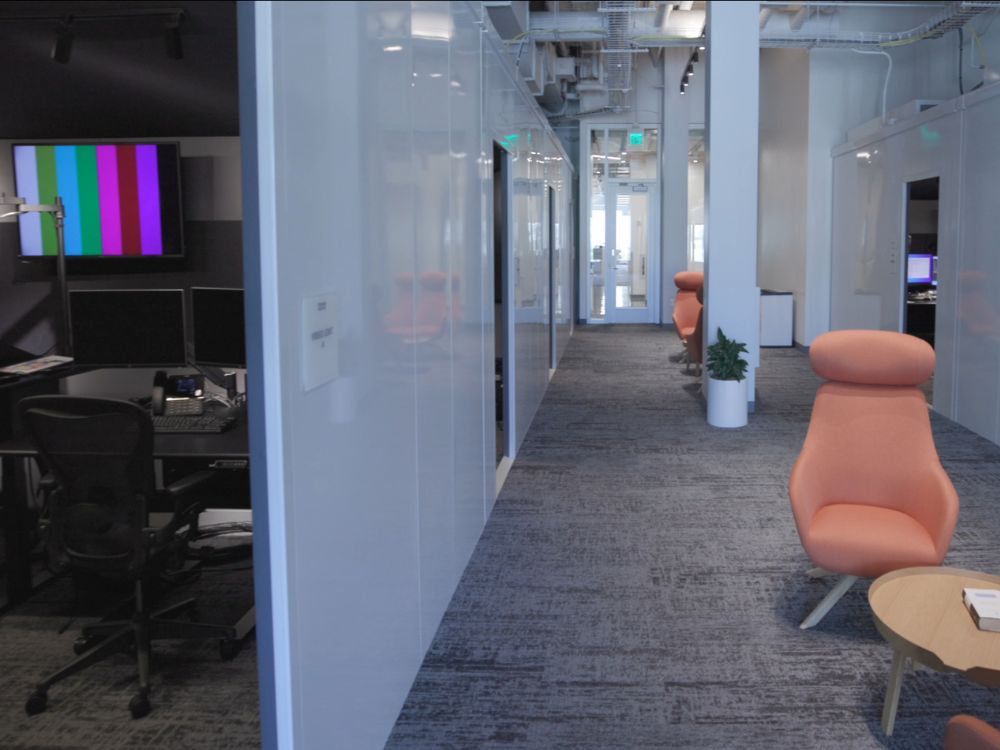
13. Professional Studios / Recording Booths / Sound Studios
What do video game producers, music producers, and post-production services have in common? They all require rigorous acoustic environments. To create music and audio for video games and movies with the highest quality sound recordings, you need studios and sound booths that provide the required sound isolation (TL).
To put it another way, they are acoustic enclosures for arts and media. Traditionally, all studios were made of stick-built materials, but modular construction is on the rise. Modular acoustic studios are gaining momentum because of their faster lead times and their mobility.
Do you need a sound studio right now but plan on moving in 2 years to a bigger building? Not a problem if you choose to go with modular construction. They are easy to assemble and disassemble, which makes them mobile and flexible studio solutions without sacrificing acoustic performances.
STC ratings of 50 to 65 are the standard for professional studios and sound booths. The bare minimum would be STC 45, depending on the external environment of your studios or booths.
Download our Prefabricated Modular Studios & Sound Booths brochure and/or read our Broadcasting Studios for Digital Media Production case study.
Look below at some other custom studios and sound booths Mecart manufactured in the past:

14. Noise Barrier or Barrier Walls
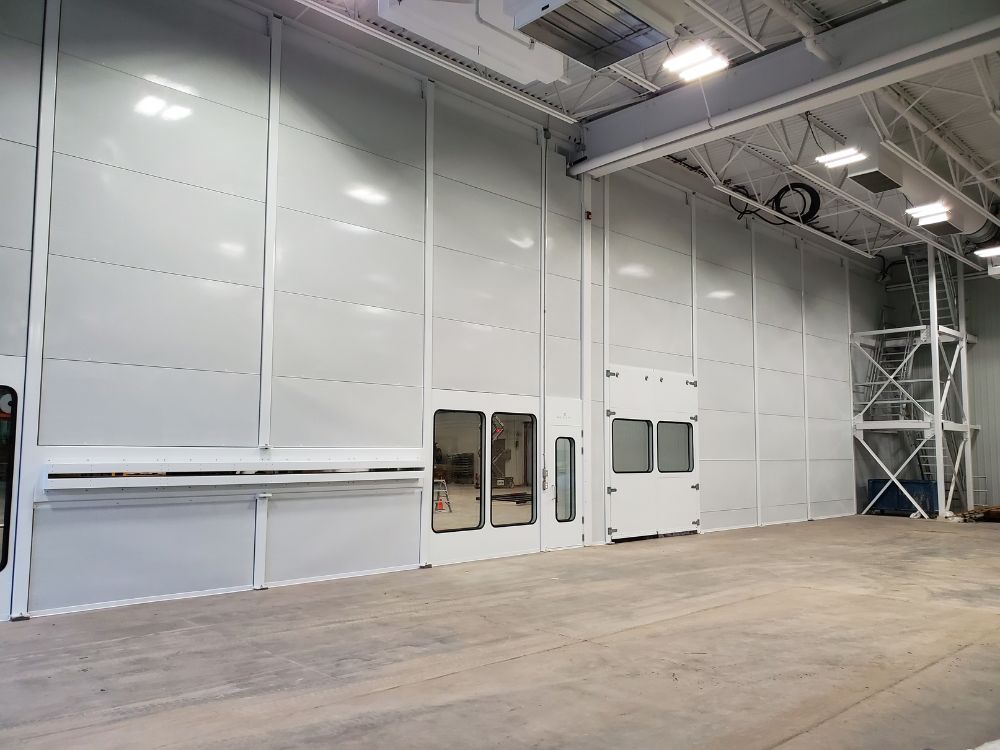
Noise barriers or barrier walls are a type of acoustic enclosure made with a modular panel system that is usually used to reduce outdoor noise. It’s mainly used to control industrial or mechanical noise, transportation-related noise, and any other disturbing noise caused by air handling units (AHU), transformers, compressors, HVAC, and more!
There is no roof or ceiling on noise barriers, making it a partial acoustic enclosure. Even though it’s mostly for outdoor noise, it’s possible to use barrier walls inside a manufacturing plant to isolate the noise source from the employees.
For example, a textile company called Mecart to obtain an acoustic wall covering the facility’s entire width, as seen in the picture on the right. The textile factory decided to isolate the machines and thus reduce the noise emanating from them.
A few doors and windows were inserted into the barrier wall to let employees oversee production activities and quickly travel through the plant. The fact that the acoustic steel wall had to contain an entrance where merchandise could move from the noisy side of the shop to the quiet side was the challenge in this project. Mecart designed an acoustic tunnel that effectively absorbed the noise rather than spread into the employee area.
To learn more, read the barrier wall case study.

15. Audiology Booths / Audiology Rooms
An audiology booth, also known as an audiometric booth or audiometry booth, is a small acoustic enclosure used by the audiologist to conduct hearing tests. Audiology booths come in different sizes, but most of the time, they have standards regarding size, and even if they are custom-made, they remain one of the smaller acoustic enclosures on the market. In fact, some can fit through a standard doorway.
These booths require good quality acoustic performances because hearing test results can be impacted by a poor acoustic environment.